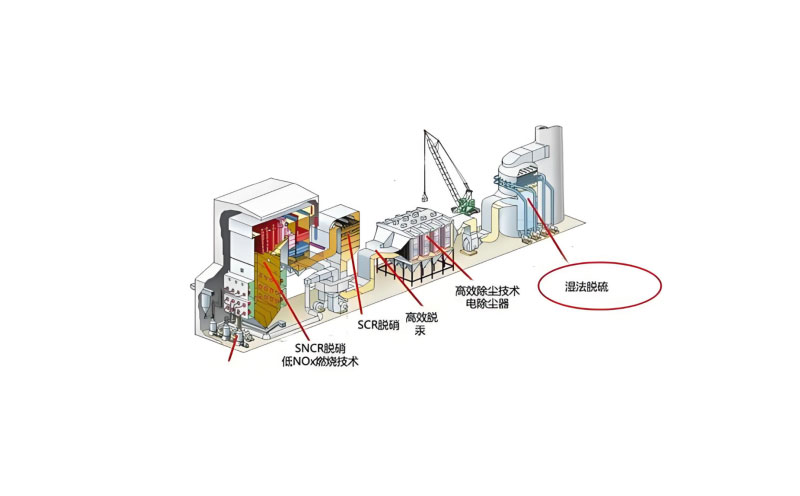
Wet desulfurization
Wet flue gas desulfurization is a commonly used flue gas desulfurization technology. Its basic principle is to use alkaline absorbents to react with sulfur dioxide in flue gas to generate gypsum or other by-products, thereby achieving the purpose of removing sulfur from flue gas. The following are the main steps and characteristics of wet flue gas desulfurization:
Flue gas treatment. The flue gas is first dedusted by a dust collector and then enters the absorption tower.
Absorbent preparation. Limestone or lime is mixed with water to form a slurry as a desulfurization absorbent.
Desulfurization reaction. In the absorption tower, sulfur dioxide in the flue gas reacts with calcium carbonate in the slurry to generate calcium sulfite, which is then oxidized to calcium sulfate and releases sulfur dioxide to achieve the purpose of desulfurization.
By-product generation. The calcium sulfate (gypsum) generated by the reaction is precipitated from the solution and can be further processed and utilized. Flue gas purification. The flue gas after desulfurization passes through a demister to remove the droplets carried, and then is heated by a heat exchanger and discharged.
The advantages of wet desulfurization technology include high desulfurization efficiency, fast reaction speed, reliable equipment operation, etc., but it also has disadvantages such as wastewater treatment problems, large initial investment, and high operating costs. Different types of wet desulfurization technologies, such as limestone-lime method, magnesium method, seawater method, double alkali method, ammonia method, etc., use different alkaline absorbents to contact with flue gas to absorb sulfur dioxide, and will also produce different by-products.